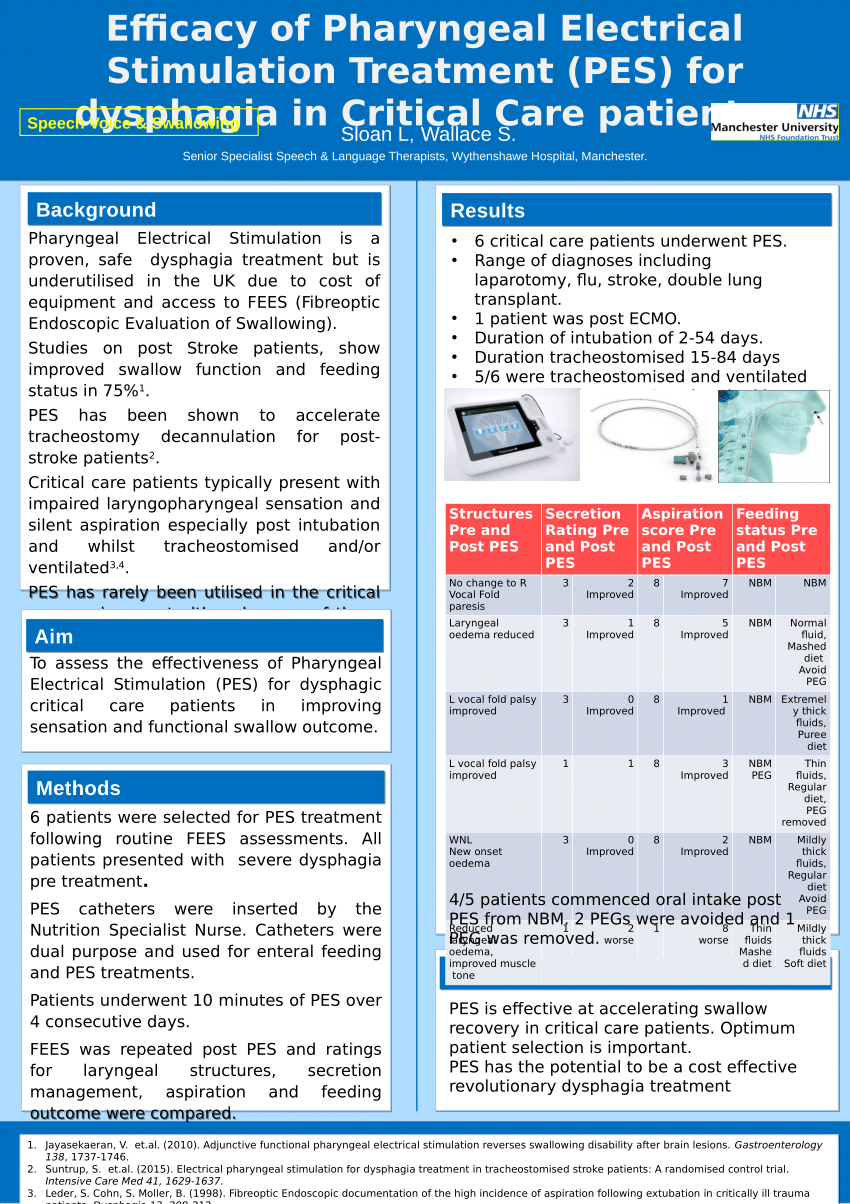
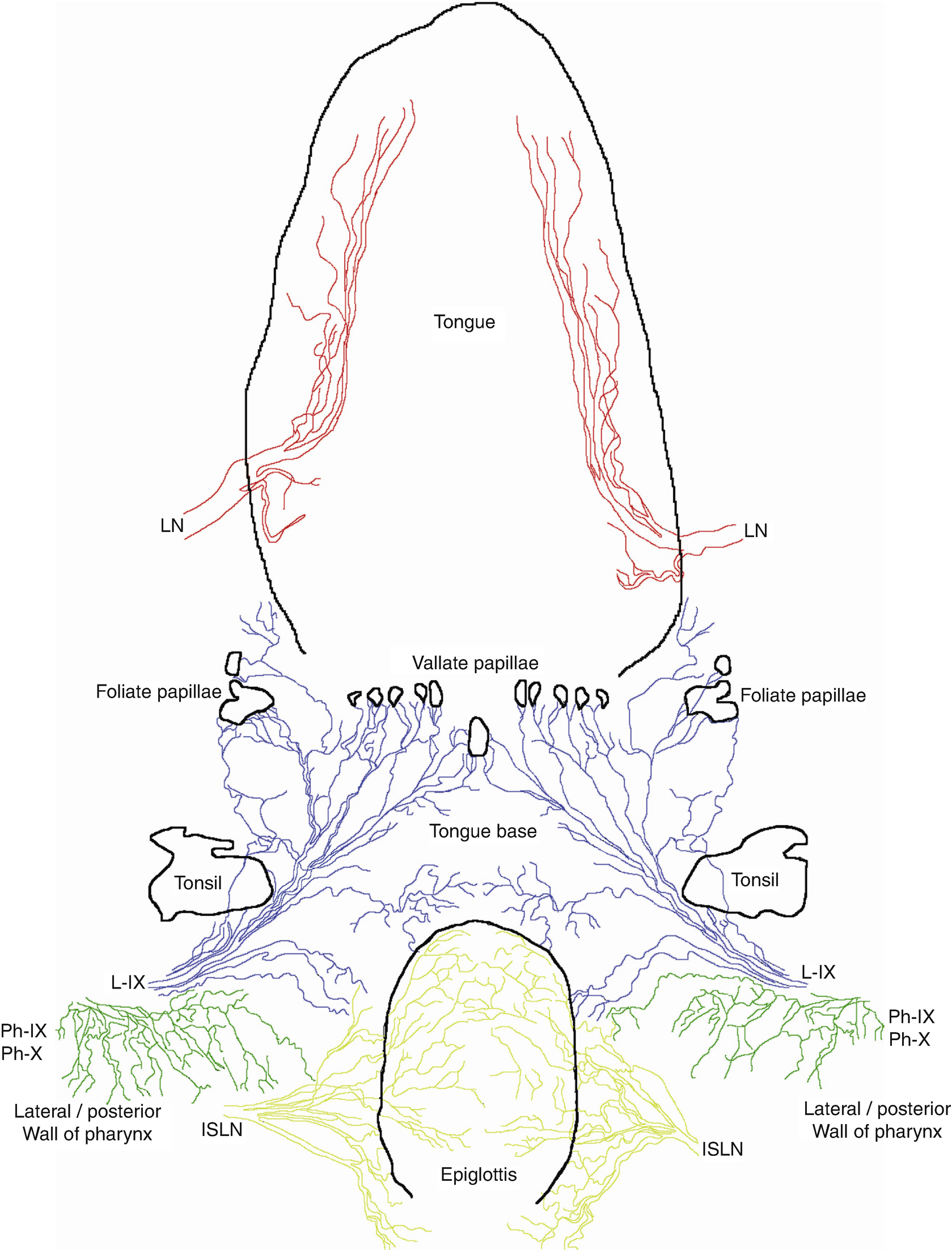
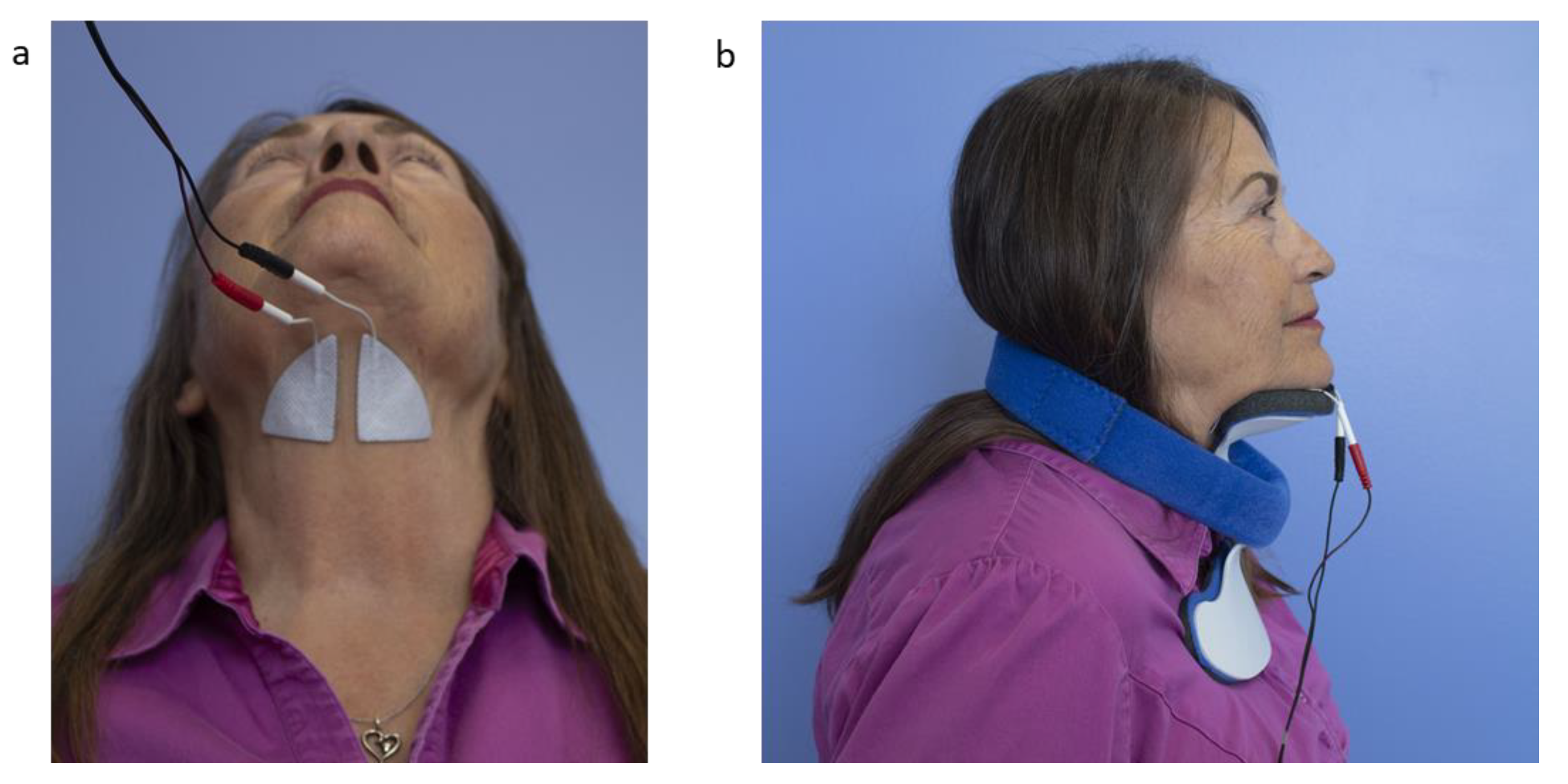
Pharyngeal electric stimulation pes is a novel treatment for poststroke dysphagia that has shown promise in 3 pilot randomized controlled trials.
Pharyngeal electrical stimulation for dysphagia.
In normal volunteers and patients with subacute stroke and dysphagia pharyngeal electrical stimulation pes at 5 hz and 75 of maximum tolerated intensity typically 10 20 ma for 10 minutes produced the strongest effect on brain excitability measured with transcranial magnetic stimulation tms.
A randomized controlled trial.
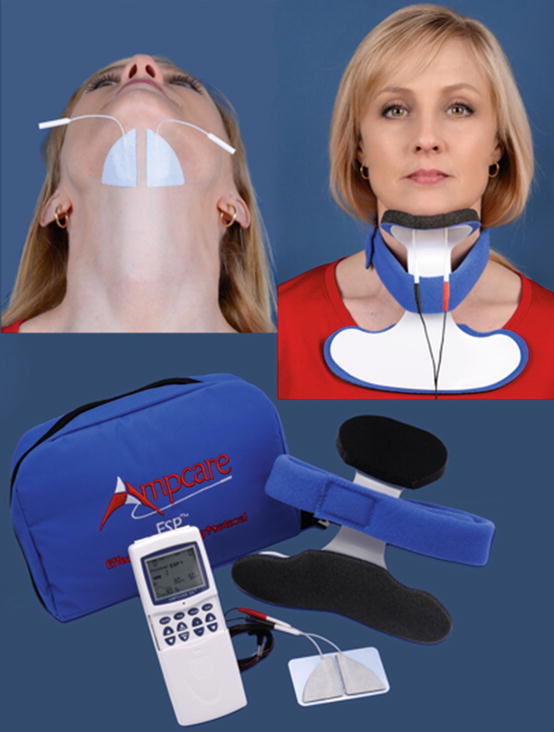
The phagenyx base station delivers the optimal stimulation for a particular patient.
Phagenyx consists of a base station and a treatment catheter which in combination enable the healthcare professional to deliver personalised dysphagia treatment for every patient.
Methods we randomly assigned 162 patients with a recent ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke and dysphagia defined as a penetration aspiration score pas of 3 on video fluoroscopy to pes or sham.
Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the u s.
We therefore postulated that low frequency 5 hz intraluminal pharyngeal electrical stimulation may improve disrupted swallowing in ms.
Research design and methods.
Pharyngeal electrical stimulation pes is a novel technique intended to activate the peripheral sensory afferents to the central pattern generator and to the cortical swallowing area by a.
In this pilot study we evaluated the effect of 5 hz pharyngeal electrical stimulation on swallowing function in twenty dysphagic and aspirating ms patients.
Irrespective of the modality of neurostimulation applied most of these studies focussed on mild to moderate stroke and included only a small proportion of severely dysphagic patients i e.
Phagenyx base station.
Pharyngeal electrical stimulation pes is a novel rehabilitation treatment for nd.
The pharyngeal electrical stimulation for early decannulation in tracheotomised stroke patients with neurogenic dysphagia phast trac trial was designed to replicate validate and extend this single centre experience in a larger phase 3 design.
Pes is carried out via location specific intraluminal catheters that are introduced transnasally and enable clinicians to stimulate the pharynx directly.
Pharyngeal electrical stimulation evaluation for dysphagia after stroke pheed the safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators.
It also records and stores patient information to avoid errors in treatment.